Evolution of Windows OS
Introduction
Microsoft Windows is a graphical operating system developed and published by Microsoft. It provides a way to store files, run the software, play games, watch videos, and connect to the Internet, etc. Windows has seen various significant versions since its first release in 1985. More than 29 years after the fact, Windows looks altogether different yet by one way or another acquainted with components that have to endure the trial of time, increments in processing power and — most as of late — a move from the console and mouse to the touchscreen. Microsoft Windows was first presented on November 10, 1983. Over twelve modifications of Windows were released from that point onward, including the present rendition, Windows 10.
Editions of Windows
Beginning with Windows XP, Microsoft has distributed different editions of Windows. Every one of these Windows versions has the same core operating system, however, a few releases have extra features, at an extra expense. Microsoft presented an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985, as a graphical working framework shell for MS-DOS because of the developing interest for graphical UIs (GUIs).The latest form of Windows for PCs, tablets, cell phones, and installed devices in Windows 10. The latest version for server PCs is Windows Server, (1903). A particular version of Windows as well runs on the Xbox One computer game support. Here’s a brief description at the history of Windows from oldest versions to the latest arrival,
Version History
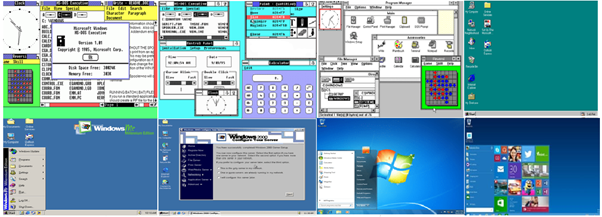
Windows 1
Windows 1.0, the main variant, released in 1985 The historical backdrop of Windows goes back to 1981 when Microsoft began to take a shot at a program called “Interface Manager”. The name “Windows” was announced in November 1983, however, Windows 1.0 was not released until November 1985. Windows 1.0 was to contend with Apple’s operating system however reach little popularity. Windows 1.0 is not a total working framework; rather, it extends MS-DOS. Windows 1.0 doesn’t allow overlapping windows. Just modular dialog boxes may show up over other windows. Microsoft sold as included Windows Advancement libraries with the C development environment, incorporated various windows samples.
Windows 2
Windows 2.0 is a 16-bit Microsoft Windows GUI-based operating environment that was released on December 9, 1987, and the successor to Windows 1.0. It includes a few upgrades to the UI and memory of the executives. Windows 2.03 changed the operating system from tiled windows to overlapping windows. Windows 2.0 additionally presented increasingly advanced console shortcuts and could utilize extended memory. Windows 2.1 was released in two unique versions: Windows/286 and Windows/386.In addition to full Windows-packages, there were runtime-only versions that sent with early Windows software from outsiders and made it possible to run their Windows software on MS-DOS. Even the earliest Windows versions already assumed many typical operating system functions; having their own executable file format and giving their own device drivers (a timer, graphics, printer, mouse, keyboard and sound).
Windows 3
Windows 3.0 was released in May 1900 offering better icons, performance and advanced graphics with 16 colors designed for Intel 386 processors. This version is the first release that provides the standard “look and feels” of Microsoft Windows for many years to come. Windows 3.0 applications can run in protected mode, which gives them access to several megabytes of memory without the dedication to take enthuse in the software virtual memory scheme. Windows 3.0 also featured improvements to the user interface. Windows 3.0 is the first Microsoft Windows version to make expansive business progress, selling 2 million copies in the initial a half year. Windows 3.1, made generally available on March 1, 1992, including a facelift. Support for Windows 3.1 ended on December 31, 2001. Windows 3.2, released in 1994, is an updated version of Windows 3.1. The update was limited to this language version. Windows 3.2 was generally sold by computer producers with a ten-disk version of MS-DOS.
Windows 95
Windows 95, was released on August 24, 1995. While still remaining MS-DOS-based, Windows 95 introduced support for local 32-bit applications, plug and play hardware, pre-emptive multitasking, long record names of up to 255 characters, and provided expanded stability over its predecessors. Windows 95 introduced a redesigned with an object-oriented user interface, replacing the previous Program Manager with the Start menu, taskbar, and Windows Explorer shell. Microsoft published four OEM Service Releases (OSR) of Windows 95 which the first OSR of Windows bundled with Microsoft’s web browser, Internet Explorer. Mainstream support and extended support for Windows 95 ended on December 31, 2000.
Windows 98
Windows Driver Model, support for USB composite devices, support for ACPI, hibernation, and support for multi-monitor configurations introduced by the release of Windows 98 on June 25, 1998. Windows 98 also included integration with Internet Explorer 4 through Active Desktop and other aspects of the Windows Desktop Update. In May 1999, Microsoft released Windows 98 Second Edition. Mainstream support for Windows 98 ended on June 30, 2002, and extended support for Windows 98 ended on July 11, 2006.
Windows ME
On September 14, 2000, Microsoft released Windows Me (Millennium Edition), the last DOS-based version of Windows. Windows Me incorporated visual interface improvements had faster boot times than previous versions expanded multimedia functionality (including Windows Media Player 7, Windows Movie Maker, and the Windows Image Acquisition framework), additional system utilities, for example, System File Protection and System Restore, and updated home networking tools. However, Windows Me was faced with analysis for its speed and instability, along with hardware similarity issues and its removal of real mode DOS support.
Windows XP
The next significant version was released on October 25, 2001. The Windows XP pointed to unify the consumer-oriented Windows 9x series with the architecture presented by Windows NT, a change that Microsoft promised would provide better execution over its DOS-based predecessors. Windows XP would also introduce an updated user interface multimedia and networking features, Internet Explorer 6, joining with Microsoft’s.
NET Identification services, modes to help give similarity programming with software designed for all versions of Windows and remote assistance.
The two most common editions of Windows are Windows Home and Windows Professional.
◾Windows Home
Windows Home is the basic edition of Windows. It gives all the basic elements of Windows, such as connecting to the Internet, browsing the web, watching videos, using office software, and playing video games. It is the least expensive edition of Windows, and it comes preinstalled on many new computers.
◾Windows Pro
Windows Professional is an enhanced Windows edition, for power users, and small to medium-sized businesses. It includes all the features of Windows Home, in addition, Remote Desktop, Bitlocker, Trusted, Boot, Hyper-V, Windows Sandbox, Group policy management.
For Windows XP, Mainstream support ended on April 14, 2009, and Extended support ended on April 8, 2014.
Windows Vista
After a protracted improvement process, Windows Vista was released on November 30, 2006, for volume licensing and January 30, 2007, for consumers. It contained a number of new features user interface to significant technical changes, with a particular focus on security features. It was accessible in various versions and has been subject to some analysis, such as a drop of performance, longer boot time, criticism of new UAC, and stricter license agreement. Vista’s server counterpart, Windows Server 2008 was released in mid-2008.
Windows 7
On July 22, 2009, Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 were released as RTM while the previous was released to the public on October 22, 2009. Unlike its predecessor, Windows Vista, which introduced an enormous number of new features, Windows 7 was intended to be a more focused, incremental upgrade to the Windows line, with the objective of being compatible with applications and equipment with which Windows Vista was at that point perfect. Windows 7 has multi-touch support, a redesigned Windows shell with an updated taskbar, a home networking system called Homegroup, and performance updates.
Windows 8
Windows 8, was released generally on October 26, 2012. It features new programming and technology that makes run faster than the previous versions. It also has a more streamlined look and feels. Windows 8 includes a tablet interface that uses large tiles t, called Metro, which is compatible with touch interactions and stills offers access to the traditional Windows desktop. Microsoft will implement Windows 8 end of life in January 2023, meaning it will discontinue all support, including paid support, and all updates. However, the operating system is in an in-between phase known as extended support. After years of confusing consumers with multiple, slightly different versions of the same operating system, Microsoft announced today that Windows 8 will come in only four versions: One for home use, one for business, one for devices running ARM chips, and one for large enterprises. An update to Windows 8, called Windows 8.1, was released on October 17, 2013, and includes features such as new live tile sizes, deeper OneDrive integration, and many other revisions.
Windows 10
Windows 10 was released on July 29, 2015. One of the primary aims of Windows 10 is to unify the Windows experience across multiple devices, such as desktop computers, tablets, and smartphones. As part of this effort, Microsoft developed Windows 10 Mobile alongside Windows 10 to replaces Windows Phone — Microsoft’s previous mobile OS. Changes on PC include the return of the Start Menu, a virtual desktop system, and the ability to run Windows Store apps within windows on the desktop rather than in full-screen mode. Windows 10 includes online versions of OneNote, Word, Excel and PowerPoint from Microsoft Office. The most secure Windows ever, Windows 10 provides antivirus, firewall, ransomware, and Internet protections, all built-in, at no extra cost. The terms closely follow Microsoft’s pattern for other recent operating systems, continuing the policy of five years of mainstream support and 10 years of extended support. Mainstream support for Windows 10 will continue until Oct. 13, 2020, and extended support ends on Oct. 14, 2025.
Windows Operating Systems Timeline

